Cat No.:61003 ★Download Datasheet★
Size: 24 tests/box
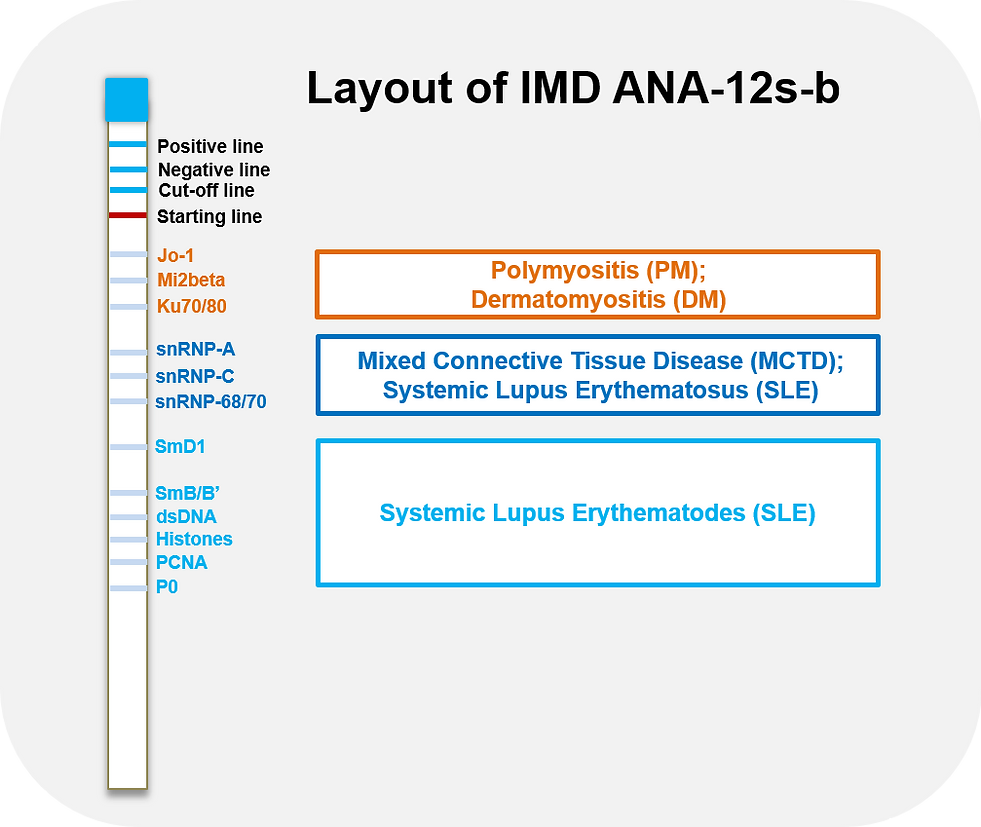
Introduction
Antinuclear antibodies (ANA) are a group of autoantibodies that specifically target substances in the nucleus of cells. One group of ANAs represent autoantibodies against extractable nuclear antigens, such as SS-A/Ro, SS-B/La, Sm, RNP, Scl-70 and Jo-1, which are mainly ribonucleoproteins and nuclear enzymes. Another group of ANAs are against nucleic acids (dsDNA), complexes of nuclear proteins and histones.
Detection and classification of these ANAs in human blood are important for differential diagnosis of systemic autoimmune diseases (SAD). Utilization of high-quality autoantigens for the screening and semi-quantification of specific ANAs has been routinely used in clinical practice for precision diagnosis and monitoring the progression of these diseases.
Assay Characteristics
Autoantigens | Clinical Indication |
dsDNA | SLE (highly specific marker) |
Histones | SLE; drug induced form of SLE; systemic sclerosis; rheumatoid arthritis |
SmB/B’ & SmD1 & SmD3 | SLE (highly specific marker) |
P0 & PCNA | SLE |
snRNP A & C & 68/70 (snRNPs) | MCTD (primarily isolated appearance); SLE; Sjogren’s syndrome; systemic |
SSA/Ro52 & SSA/Ro60 & SSB/La | Sjogren’s syndrome (primary, secondary); SLE (dermal forms LE); |
Jo-1 | DM/PM; increased risk of pulmonary fibrosis |
PL-7 & PL-12 | DM/PM; antisynthetase syndrome (myositis, interstitial pulmonary fibrosis, |
PmScl-75 | DM/PM; systemic sclerosis |
CENP-A & CENP-B | CREST syndrome; SSc (limited form without the appearance of antigen |
Scl-70 | SSc; overlap syndrome scleromyositis (highly specific marker) |
Unique Advantages
◆ Ready-to-use components;
◆ Simultaneous diagnosis of 7 major SADs in 1 test;
◆ Easy interpretation;
◆ Superior batch-to-batch reproducibility;
◆ Excellent specificity and sensitivity (> 95%);
◆ Rapid procedures (~ 35 minutes);
◆ Positive and negative controls;
◆ Strict quality control and clinical validation.
