Cat No.:31A030 ★Download Datasheet★
INTRODUCTION
Histones are DNA-associated cationic proteins in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells to form nucleosomes.
Anti-histone autoantibodies are present in a number of clinical conditions, primarily in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE, ~80%)
and drug-induced lupus (DIL, ~95%) by procainamide, hydralazine, chlorpromazine, and quinidine.
Additionally, these autoantibodies are also detectable in other rheumatic diseases, including myositis and systemic sclerosis (SSc).
Assay Characteristics:
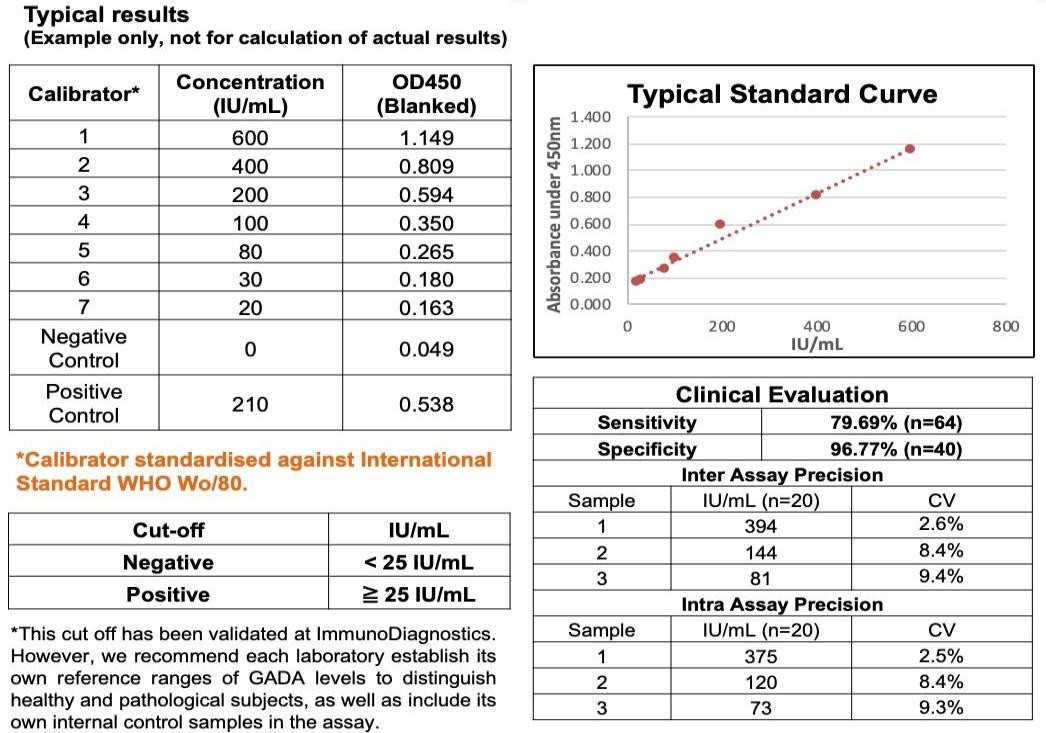

Sample Type: Serum and plasma
References:
1. Dumortier, H., & Muller, S. (2007). Histone Autoantibodies. In Autoantibodies (pp. 169-176). Elsevier.
2. Dooley, M. A. (2016). Drug-induced Lupus. In Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (pp. 473-479). Academic Press.
3. Firestein, G. S., Budd, R., Gabriel, S. E., Mcinnes, I. B., & O'dell, J. R. (2016). Kelley And Firestein's Textbook Of Rheumatology E-book.
Elsevier Health Sciences.
4. Portanova, J. P., Arndt, R. E., Tan, E. M., & Kotzin, B. L. (1987). Anti-histone Antibodies In Idiopathic And Drug-induced Lupus Recognize
Distinct Intrahistone Regions. The Journal Of Immunology, 138(2), 446-451.
5. Portanova, J. P., Rubin, R. L., Joslin, F. G., Agnello, V. D., & Tan, E. M. (1982). Reactivity Of Anti-histone Antibodies Induced By
Procainamide And Hydralazine. Clinical Immunology And Immunopathology, 25(1), 67-79.
